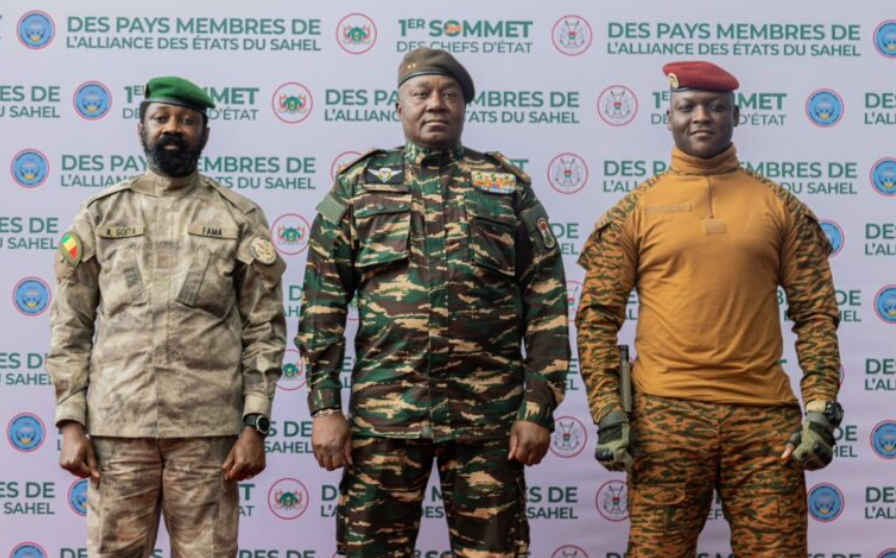
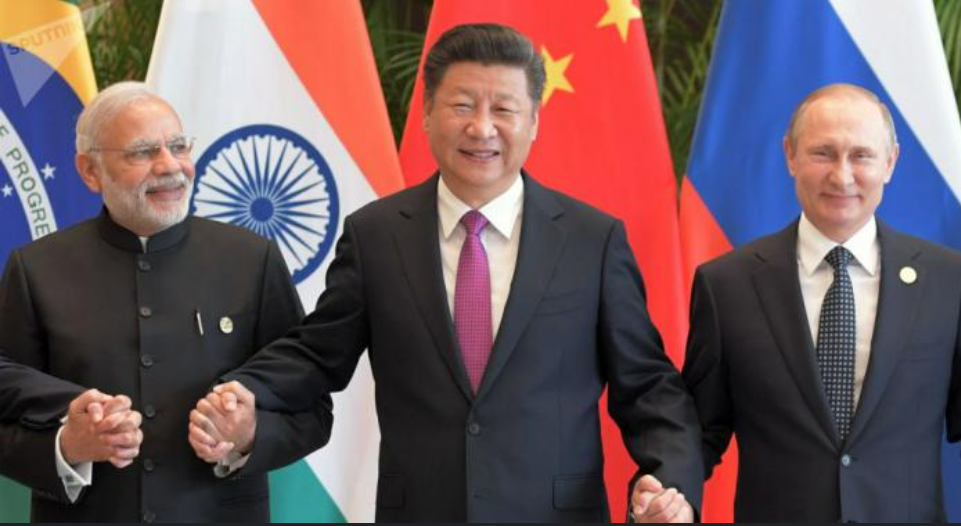
World
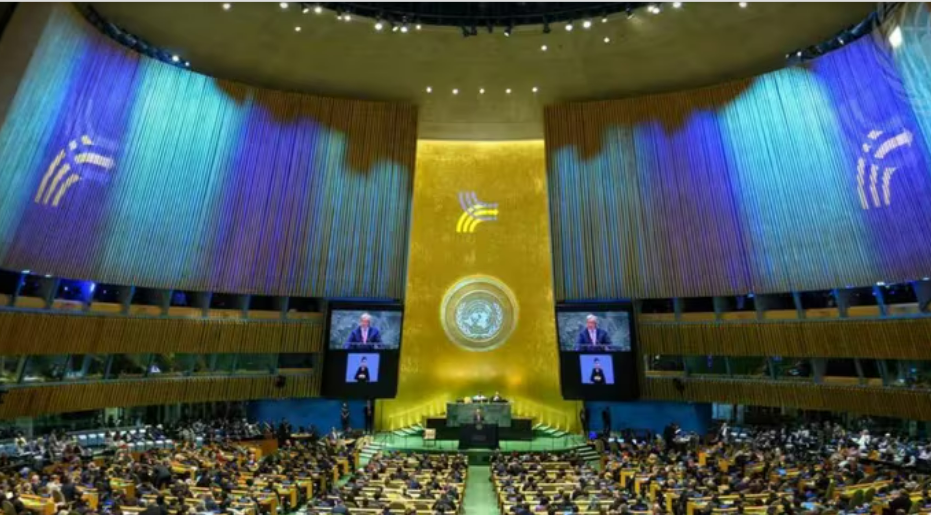

Imagen: INFOBAE
The UN approves its new Future Pact
Redacción:
The globalist agenda advances in its new version with a vision for 2045
https://500palabras.pe/en/world.php?noticias_id=20
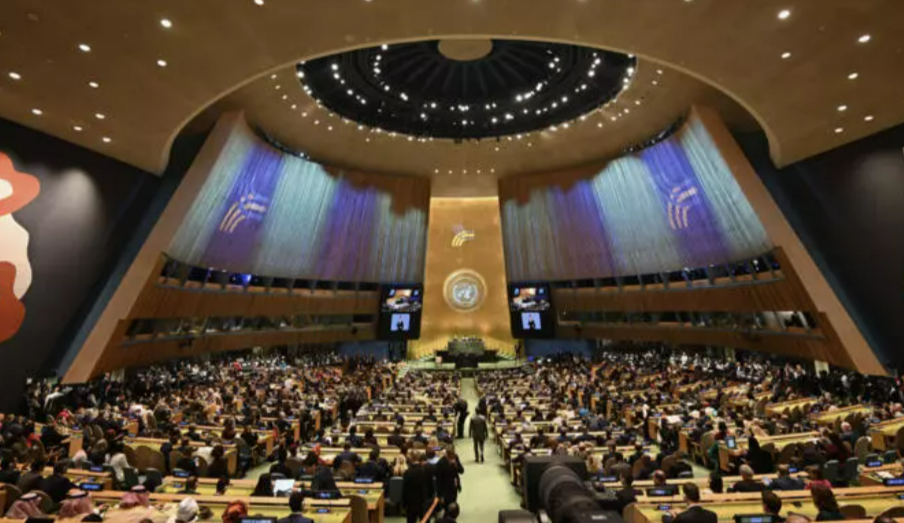
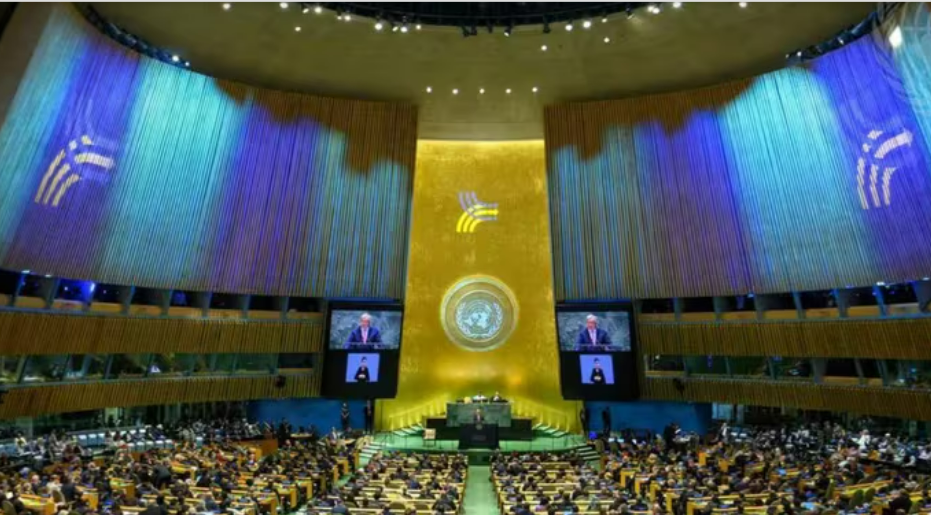
New York, September 22, 2024 World leaders have approved a Pact for the Future that includes within its sections a Digital Global Pact and a Declaration on Future Generations. The Pact for the Future is the most far-reaching international agreement of the 21st century. The agreement covers entirely new areas and aims to ensure that international institutions can fulfill their role in a changing world. According to Secretary General António Manuel de Oliveira Guterres: “we cannot create a decent future for our grandchildren with a system built by our grandparents.” The new Future Pact is a new plan designed by the UN to achieve a global agenda, in view of new challenges. The Compact for the Future agreement is a strong declaration of the countries' commitments to the United Nations, the international system and international law. The themes of this new global agreement are 56 points that deal with the following topics: - Sustainable development and development financing - International peace and security - Science, technology and innovation and digital cooperation - Youth and future generations; and - Transformation of global governance. This new pact includes modern advances that are constantly updated. According to the official UN website: "The draft can promote a multilateral system that reflects today's realities and benefits everyone, everywhere." Key Points They are goals for sustainable development, arms control and the management of new technologies, climate change and the potential threats of artificial intelligence (AI). Finally, peacekeeping. a)Peace and international law -The agreement highlights the “increase and diversification” of threats to world peace, in particular, the “risk of nuclear war” and reiterates the fundamental commitments of the members of the UN: respect for the Charter of Human Rights and of International Law, the protection of civilians and diplomacy to resolve conflicts. b) Integrated economy In this context, in a very relevant matter for the poorest countries, the Pact for the Future commits to “accelerate the reform of the international financial architecture” (action 47), in particular to allow some excluded States to more easily access financing from development banks, investing in development objectives and preparing for the impacts of climate change. These reforms will require decisions such as the IMF and the world bank c) Artificial intelligence Along with the main document of the new pact, Member States also adopted the "Global Digital Pact to reduce the digital divide and develop safe and respectful technologies for the benefit of all." d) Peace and nuclear weapons The agreement highlights that the “increase and diversification” of threats to world peace are constant, and places particular emphasis on the “risk of nuclear war.” Likewise, it reiterates the fundamental commitments of the members of the UN: respect for the Charter of Human Rights and International Law, the protection of civilians and diplomacy to resolve conflicts. Finally, it also reiterates the commitment to the elimination of nuclear weapons. And the Agenda2030? The new pact ratifies the objectives of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, adopted in 2015, but assumes that they cannot be met at that time point and postpones the deadline of these global objectives to 2045. Agenda 30 proposes 17 objectives with 169 goals of an integrated and indivisible nature that cover the economic, social and environmental spheres. The so-called SDG = Sustainable Development Goals. The pact promises to accelerate efforts to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals, which seek to eradicate extreme poverty, fight hunger, achieve gender equality and promote education by 2030. They are goals for sustainable development, arms control and the management of new technologies. Countries against and Abstentions The "Future Pact" was not approved by consensus and not unanimity; resistance was shown by some countries. 143 countries in favor and against, there were seven votes.